After going remote, this team operated at just 79% of their in-office productivity levels – contrasting sharply with our case study published two weeks ago.
This calls into question the effectiveness of remote work for some teams' performance.
Our ongoing research indicates that several factors can affect a team's remote work productivity. Team size appears to be key.
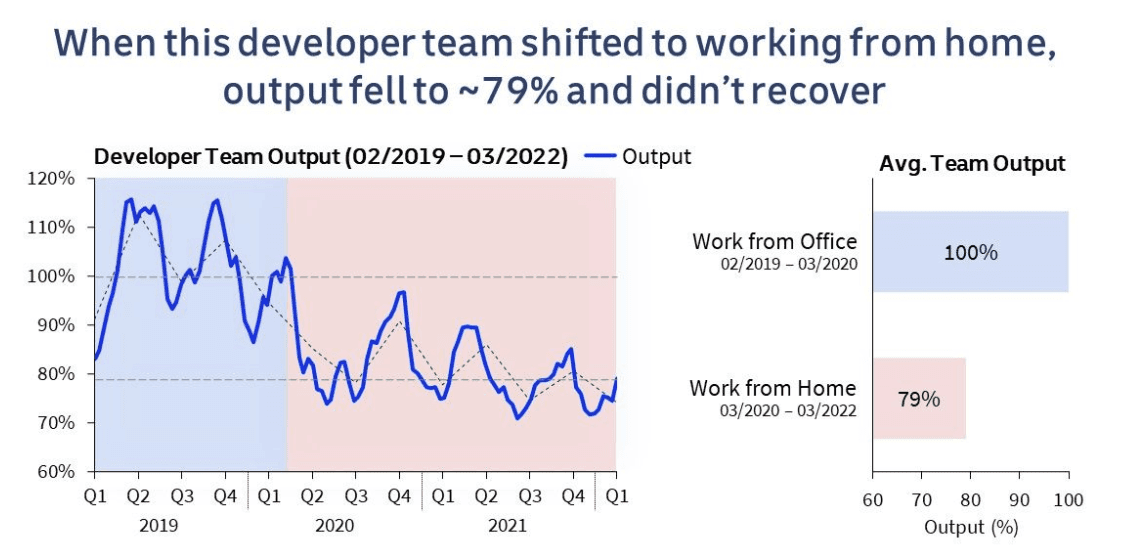
Given the variability we see among even similar teams, the best approach is to examine your own productivity data.
Snapshot of Our Study:
- Period Analyzed: Feb 2019 – Mar 2022
- Industry: Retail Tech
- Service: Shopping Rewards Platform
- Team Size: 18 Developers
- Languages: PHP, JS
- Location Pre-COVID: Silicon Valley, USA
- Location Post-COVID: Dispersed, USA
Methodology:
Leveraging a cutting-edge algorithm developed at Stanford, we can objectively measure a developer's productivity based on the functionality of their source code. This algorithm scans through Git & code repositories, quantifies the functionality of the code, and generates an impartial metric for both individual developers and teams, irrespective of programming language or coding style.
Dive Deeper:
For a comprehensive breakdown of our case study, click the link in the comments.
About Our Mission:
This is part of a Stanford research initiative aimed at quantifying software engineering output.
The goal? To enable data-driven decisions in engineering organizations.
Our research participants harness our groundbreaking algorithm's insights for pivotal decisions - be it work models, team structure, outsourcing, or tool adoption.